Author: Rimita Chakraborty
What is Single Gene Disorders?

Single gene disorders are a condition which happens due to the alteration and mutation of a specific DNA sequence of a specific gene which results in the alteration or missing sequence of protein product that the gene encodes. This type of disorder can be life threatening or sometimes it is manageable through proper treatment and medications.
Causes of Single gene Disorder:
- Mutation in a single gene
- Inherited from parents
Types of Single gene Disorder:
- Autosomal Dominant: Presence of a single copy of mutated gene in any one parent is enough for the cause of Autosomal dominant disorder . There is no existence of carriers in Autosomal dominant disorders. If one parent is having the disorder then there is a 50% chance that the disease may be inherited from the parent to offspring.
- Autosomal recessive: Females usually act as carriers for this disorder and don’t show any symptoms. To inherit Autosomal recessive inheritance both parents must carry a single copy of the mutated gene. Then the chances of a child to be affected with this disorder is 25%.
- X Linked Dominant: Mutation occurs only on the X chromosome. Both males and females can be affected but the percentage of affected males is high due to the presence of only one X chromosome. In this case Females may act as carriers and may transfer the disorder towards the next generation. X linked dominant disorders usually inherit from affected father to daughter in every pregnancy.
- Y linked : Inherited from father to son. Only the Y chromosome is affected.Also known as Holandric Inheritance. Ex- Excessive growth of hair in the outside rim of ear.
Examples of Single gene Disorder:
1. Huntington’s disease:
The main reason behind Huntington’s disease is mutation in Huntingtin gene or HTT genes. This gene contains triplet nucleotide sequence i.e. Cytosine-Adenine-Guanine (CAG) that is repeated several times within a specific region of the gene. The normal range of CAG sequence is 10-35 repeats but the person who is suffering from Huntington’s disease this repeat continuously goes on which results in the expansion beyond normal range. It is a neurodegenerative disorder. The excessive expansion of CAG repeats leads to the production of huntingtin protein which is extremely dangerous for the nerve cells of the brain because this protein destroys cellular processes which results in degeneration and cell death.
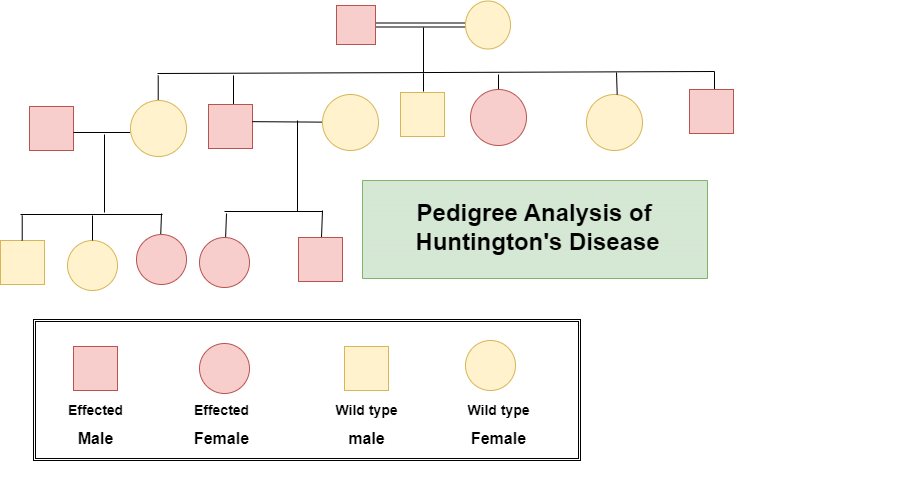
From this pedigree we can find that this Autosomal dominant trait had been inherited from the father of Generation 1. Both the males and females are affected in the next generation.
This disease comes under Autosomal dominant disorder because Huntingtin gene is present in every individual. Normal parents can have children with this disorder due to the influence of one mutated gene whereas Parents affected with this disorder can have normal children, in that case huntingtin gene is present within that children but that gene is not mutated.
2. Cystic fibrosis
The main reason behind the disease of Cystic fibrosis is the mutation of Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene or CFTR gene. This mutation causes disruption in the chloride channel. In normal person CFTR gene instructs this chloride channel to transport all the negatively charged chloride ions, a component of common salt i.e. Sodium chloride and thus all this ions are found in sweat. The mutation in CFTR gene prevents the flow of chloride ions and water across cell membranes which results in the formation of thick mucus that blocks the airways of various ducts which causes difficulty in breathing, poor growth and infertility in males. We can diagnose Cystic fibrosis through Sweat testing, genetic testing etc. This disorder is most common in the northern parts of the European region. The people who are suffering from this disorder can survive upto 50 years. Autosomal recessive inheritance pattern is found in this disorder.
3. Sickle cell disease
The main reason behind Sickle cell disease is the mutation of Hemoglobin Subunit Beta gene or HBB gene. HBB gene is present in chromosome 11p15.5 , which gives instructions for the formation of the beta-globin chain that is responsible to carry oxygen in red blood cells. Beta-globin is a component of Hemoglobin. Mutation in the HBB gene helps in the formation of abnormal versions of Hemoglobin also known as HBS. This mutation also results in the change of sixth sequencing of amino acid in the chain from glutamic acid to valine which results in the sticking of Hemoglobin molecules together and the formation of rods. These rods helps in the transformation of red blood cells to take deformed sickle shape which leads to various complications including anemia.
Here we can observe autosomal recessive patterns of inheritance. Individuals with one copy of abnormal HBB gene and one copy of normal HBB gene can make them carriers. The affected individuals are having altered genes from both the parents. Some symptoms of Sickle cell disease are observed from childhood such as pain, chronic hemolytic anemia, severe infections etc. To diagnose sickle cell disease laboratory test such as: Hemoglobin electrophoresis, High performance liquid chromatography etc. are used to detect the presence of HBS in blood.
4. Duchenne muscular dystrophy
The main reason behind Duchenne muscular dystrophy is the mutation of the DMD gene , located on the X chromosome. Here we can observe X linked recessive inheritance pattern. This gene is essential for a normal person to maintain the structural integrity of muscle cells. DMD gene is responsible for producing Dystrophin protein. The mutation in DMD gene causes lack of Dystrophin protein which results in the formation of fragile muscle cells that can be easily damaged. This situation results in muscle degeneration and muscle weakness. Symptoms include: Difficulty in climbing stairs, deficulty in walking etc. Treatment like Gene therapy, exon skipping etc will be helpful for them.
Management and Treatment:
- Symptom management with the help of medication
- Dietary changes
- Enzyme replacement Therapy
- Gene therapy
- Genetic counseling: Genetic Counselor can predict the risk of passing the disorder to future generations and they can aware the patient about the risk and other factors about the disorder.
- Early diagnosis with the help of genetic testing can help to manage better
- Surgical intervention
Conclusion:
Awareness about the inheritance pattern of single gene disorder is very essential for the overall well-being of an individual due to various reasons:
- Prediction on the genetic disorder of upcoming offspring will guide in the decision of family planning
- Early diagnosis can help to prevent all kinds of genetic disorder very effectively
- Understanding the inheritance pattern help genetic counselor to inform individuals about their health and of their family so they can make informed decisions
- Research on single gene disorders will help in the advancement of medical science, and gene therapy
- It will promote public health , and genetic screening programs which will result in overall wellbeing of individuals and their families who are affected with these diseases.
Future prospects:
The future of single gene disorder research is very promising due to the development of technologies like Crispr Cas 9 gene editing and Next generation sequencing.
In 2023 Crispr Cas 9 had already created a revolution in genomics research. The first drug Casgevy was developed with the help of Crispr Cas 9 to cure Sickle cell and Beta Thalassemia disease. Crispr Cas 9 technologies will advance genetics research in future because of several reasons:
- It will allow researchers to create animal models with genetic mutations and single gene disorder.
- Allow researchers for the functional consequences of specific mutation that are connected with single gene disorders
- Allows genetic researchers to edit disease causing mutation which will help to develop targeted therapies
- Holding bright future for gene therapy approaches which will help for the treatment of single gene disorders
After the development of Next Generation sequencing , the molecular diagnostic techniques of Single gene disorder had been evolved because it provides a comprehensive overview about heterogeneous disorder, exome sequencing, and genome sequencing which supplies the unbiased analysis of human genome and this situation will help in the evolution towards personalized treatment.
NGS has already helped to advance research in many fields like clinical genomics, Cancer research etc. Further advancement of Next generation sequencing technologies will help for more accurate and sensitive data, and may develop cost effective solutions for more advance research.
References:
- Blencowe, H., Moorthie, S., Petrou, M., Hamamy, H., Povey, S., Bittles, A., Gibbons, S., Darlison, M., & Modell, B. (2018, August 14). Rare single gene disorders: estimating baseline prevalence and outcomes worldwide. Journal of Community Genetics, 9(4), 397–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12687-018-0376-2
- Xue, Y., Ankala, A., Wilcox, W. R., & Hegde, M. R. (2015, June). Solving the molecular diagnostic testing conundrum for Mendelian disorders in the era of next-generation sequencing: single-gene, gene panel, or exome/genome sequencing. Genetics in Medicine, 17(6), 444–451. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2014.122
- Alliance, G., & Services, N. Y. M. A. C. F. G. A. N. S. (2009, January 1). Understanding Genetics. Lulu.com.
- Grigorenko, E. (2008). Genetic Disorders: Single Gene. Encyclopedia of Infant and Early Childhood Development, 20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-012370877-9.00071-2
- Chial, H. (2008) Mendelian genetics: Patterns of inheritance and single-gene disorders. Nature Education 1(1):63
- Single Gene Disorders. (n.d.). https://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/disorders/singlegene
- Single Gene Disorders Causes & Diagnosis – FDNA Health. (2021, June 28). FDNA Health. https://fdna.health/knowledge-base/single-gene-disorders/
- What are single gene disorders? (n.d.). https://www.yourgenome.org/theme/what-are-single-gene-disorders/
- Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Genetic Disorders. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21751-genetic-disorders
- What are Single Gene Disorders? (2022, November 17). News-Medical. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Single-Gene-Genetic-Disorder.aspx
- Bangla, T. (2021, October 19). Inherited Diseases: ৫টি সাধারণ জিনঘটিত রোগ, যা আপনার জানা উচিত. TV9 Bangla. https://tv9bangla.com/photo-gallery/5-common-genetically-inherited-diseases-439274-5.html
- জেনেটিক ডিসঅর্ডার সম্পর্কে ব্যাখ্যা কর বিড়লা ফার্টিলিটি এবং আইভিএফ. (2022, October 10). Birla Fertility & IVF.
- Examples of Single Gene Disorders. (n.d.).
- Padiath, Q. S. (2024, March 18). Inheritance of Single-Gene Disorders. MSD Manual Consumer Version. https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-in/home/fundamentals/genetics/inheritance-of-single-gene-disorders
- Genetic Disorders. (n.d.).
- S. (n.d.). How Is Cystic Fibrosis Inherited? StoryMD.com. https://storymd.com/journal/pwgr5xoc4j-cystic-fibrosis/page/r5e94hnra4-how-is-cystic-fibrosis-inherited
- Moawad, H. (2021, February 12). Symptoms of Huntington's Disease. Verywell Health. https://www.verywellhealth.com/huntingtons-disease-symptoms-5091956
- Hk5w, N. L. (n.d.). Pre-implantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic / Single Gene Disorders (PGT-M). https://www.hkarc.com.hk/Pre-implantation_Genetic_Testing_for_Monogenic_Single_Gene_Disorders_PGT-M_en.html
- B. (2022, July 4). Given below is the pedigree of sickle cell anaemia- in a family -In this the RBC of both parents will be –. https://byjus.com/question-answer/given-below-is-the-pedigree-of-sickle-cell-anaemia-in-a-family-in-this-the-10/
- Ramzan, A. (2022, July 22). What is sickle cell anemia? https://amirramzan8.blogspot.com/2022/07/sickle-cell-anemia-introduction-people.html?m=1
